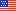
Migraine is a Common Condition
Image
History and Physical Exam
Image

- Graduate student
- Increasing headache frequency for past 2-3 months
- Headaches occur daily and disrupt coursework and studying
- Some headaches are severe with nausea and light sensitivity
- Some are mild headaches
- Associated neck pain and muscle tension
Medical History Interview
Joe describes his history of headache.
Test Your Knowledge
What kind of headaches do you think Joe is having?
Incorrect
Incorrect
Incorrect
Incorrect
Incorrect
Incorrect
Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Incorrect
Criteria for Migraine Without Aura
International Criteria for Headache Disorders 3 (ICHD3)
(required) A
- >5 attacks filling criteria B-D
(required) B
- Last 4-72 hours
(at least 2) C
- Unilateral location
- Pulsating quality
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Aggravated by or causes avoidance of routine physical activity
(at least 1) D
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Photophobia and phonophobia
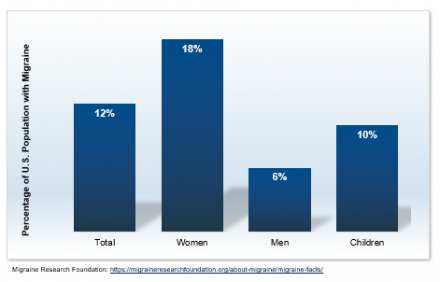
4 Nonobligatory Phases
Migraines are associated with 4 nonobligatory phases.
Image
Not all patients experience all four of these phases.
Test Your Knowledge
Joe’s headaches were infrequent and now occur daily. He is concerned that his headache is being caused by a brain tumor. So he thinks he needs a CT scan. True or false: Joe should get a CT scan.
Incorrect
Incorrect
Correct
Correct
SNOOP Criteria
The SNOOP criteria list worrisome headache red flags that may indicate need for MRI.
- Systemic symptoms (fever, weight loss) and/or Secondary risk factors (HIV, cancer)
- Neurologic symptoms or abnormal signs (confusion, ↓ alertness, impaired consciousness)
- Onset: sudden, abrupt, or split-second
- Older age: new onset and progressive headache
- Positional headache, papilledema, or prior headache now worsening
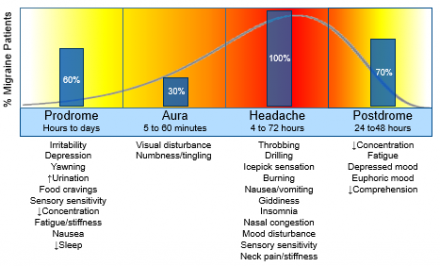
Episodic Migraine
Episodic migraine headaches may transform into chronic migraine.
Image
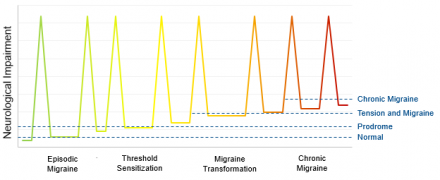
Risk Factors for Chronic Migraine
Several factors increase risk for chronic migraine:
- Female Gender
- Obesity
- Anxiety and depression
- Head injury
- Sleep apnea
- Medication overuse
Thorough Medical History
A thorough medical history is the first step in diagnosing Joe’s chronic headaches.
- Full time student (spends several hours daily sitting at computer studying)
- Daily caffeine (1 cup of coffee in the AM), occasional alcohol (weekends), no tobacco or drugs
- Reports significant stress from heavy class schedule
- Since starting graduate school work, sleep and exercise habits have changed
- Irregular sleep hours
- Works late into the evening
- Limited physical activity
Physical Exam
Dr. Bernstein performs a full physical exam including neurological tests.